As explained in the presentation article, Stambia can work with Google Cloud Storage to perform operations such as creating Buckets, sending retrieving, copying, moving or deleting Blobs, defining metadata on Blobs, ...
This article demonstrates how to work with Google Cloud Storage in Stambia.
Prerequisites:You must have previously installed Google Cloud Platform connector to be able to work with Google Cloud Storage.
Please refer to the following article that will guide you to accomplish this.
Metadata
When Stambia DI Google Cloud Platform Connector is installed and configured, you can start creating your first Metadata.
This will then allow to define Google Cloud Storage information such as defining the Buckets, ...
Metadata creation
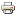
Create the Metadata, as usual, by selecting the technology in the Metadata Creation Wizard:
Click next, choose a name and click on finish.
Metadata Configuration
Google Cloud Credentials definition
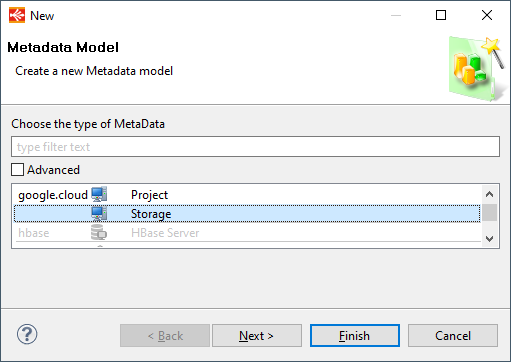
When the Metadata is created, you can start defining common information about Google Cloud Storage access
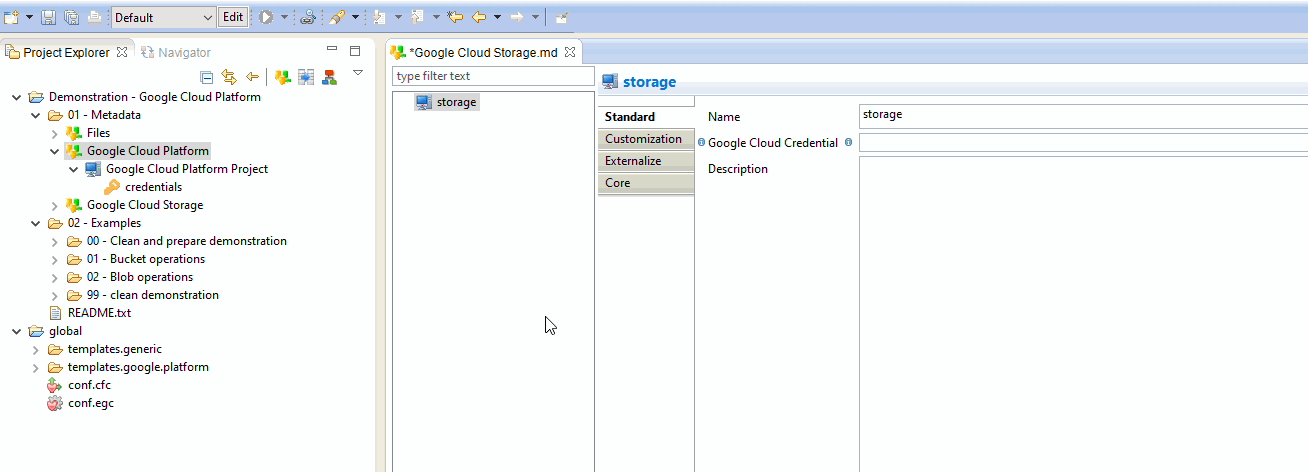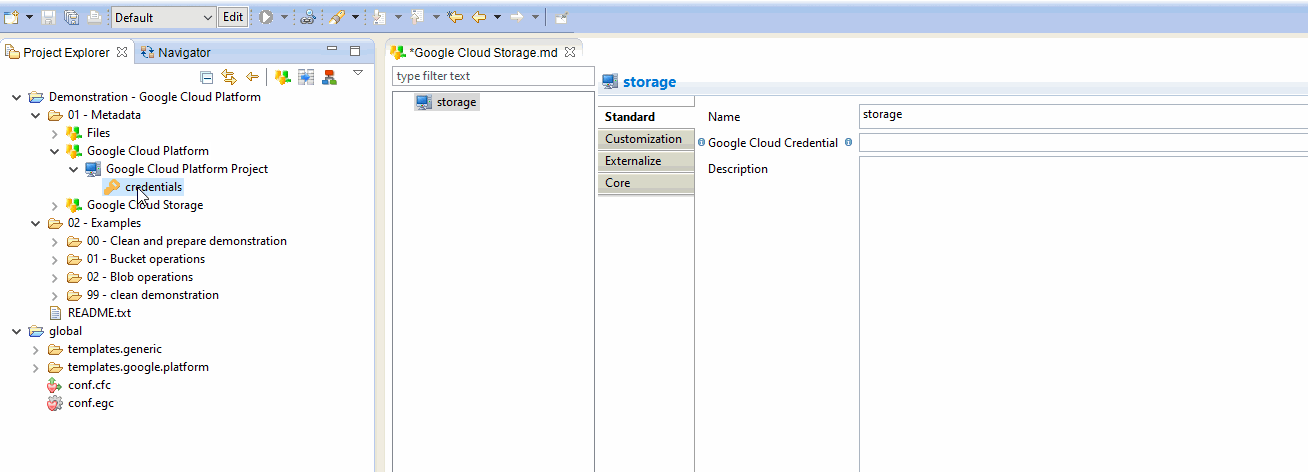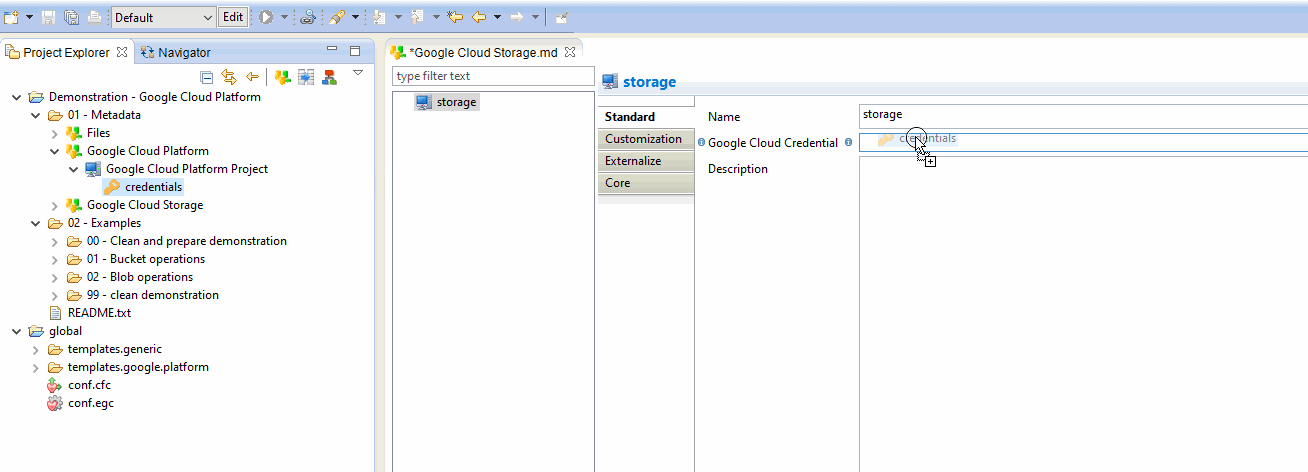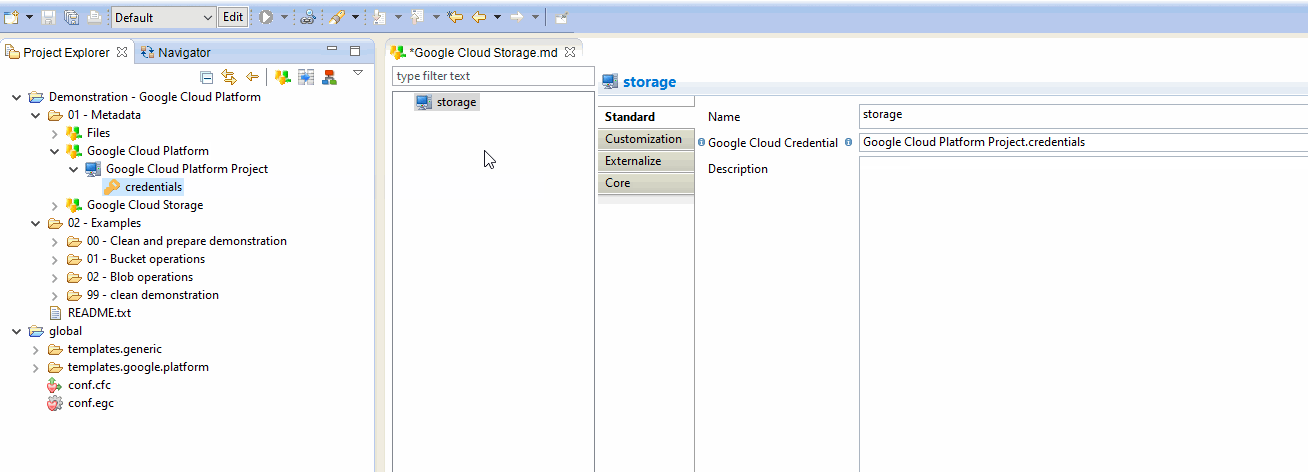
The first step is to define the Google Cloud Credentials that must be used to perform operations on Google Cloud Storage.
This is mandatory as this will be used to connect to the correct Google Cloud Project and with given credentials.
For this, simply drag and drop a credential node from a Google Cloud Platform Metadata which should have been created before.
Buckets definition
Credentials being configured, you can now start defining Buckets nodes in your Metadata.
This is just a Metadata definition, the Buckets does not necessarily need to exist physically on Google Cloud Storage.
The connector allows to create or delete Buckets easily.
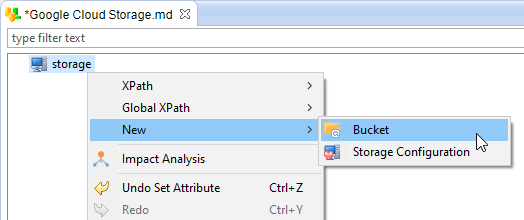
To add a new Bucket node, right click on the root node and choose "New > Bucket"
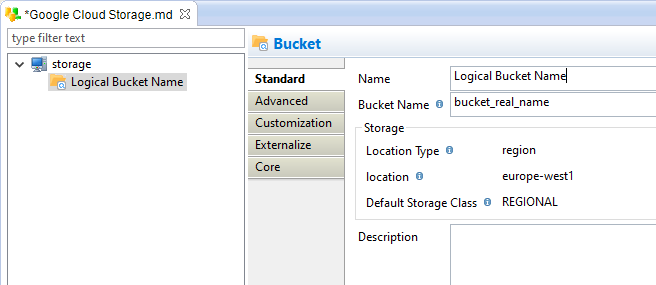
You can then define a logical name for this Bucket, and the real Bucket Name that will be used on Google Cloud Storage.
There is several additional storage information that can be defined in the standard and advanced tab, which allows to define more precisely the Bucket's properties, such as its location, its storage class, its retention period, ...
Note that those additional information will only be used when trying to create the corresponding Bucket with the tool allowing the create Bucket, and that when they are left empty, the default value from Google API is used.
On the same idea, you can define Bucket labels and Bucket Life Cycle rules which should be used to configure the Bucket at Bucket creation.
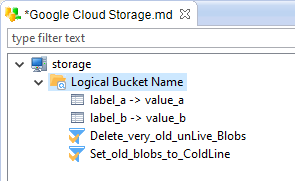
Finally, you can define 'Directories' which will be used to store and retrieve Blobs from Buckets.
This is optional and corresponds to the prefix that can be added on Blobs to organize them in virtual 'Directories'.
This will be used to filter the list of Blobs to retrieve and to create Blobs within a specific path.
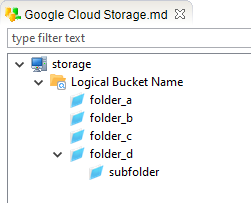
Note that you can also perform get or put operations directly on Bucket's root, this is only for organizational purposes.
Examples
Below are some examples of operations that can be performed on Google Cloud Storage.
Performing operations is quite simple, drag and drop the tool corresponding to the operation you want to perform in a Process, drag and drop the corresponding Metadata on it, and execute the Process.
A bunch of options are also available to customize more precisely the operations.
Here is a little example to create a Process for creating a Bucket:
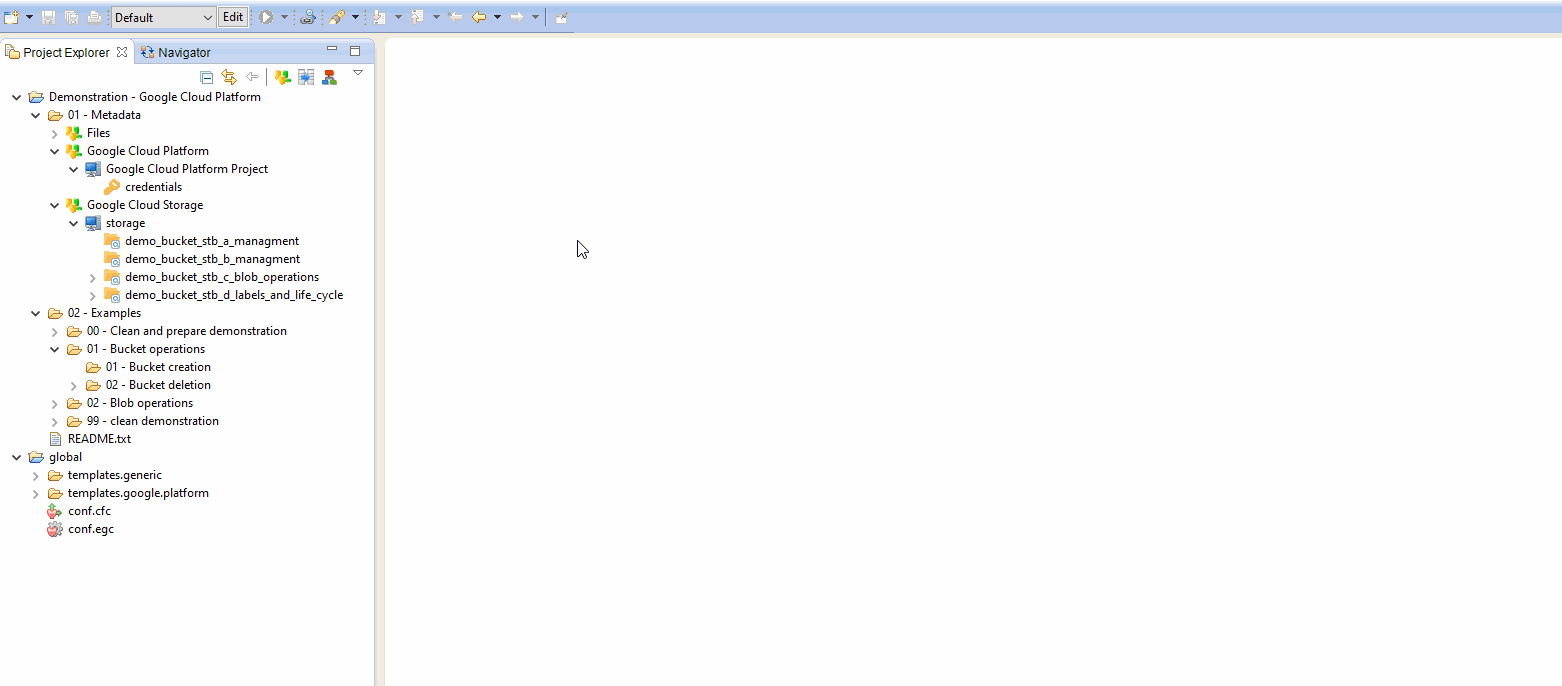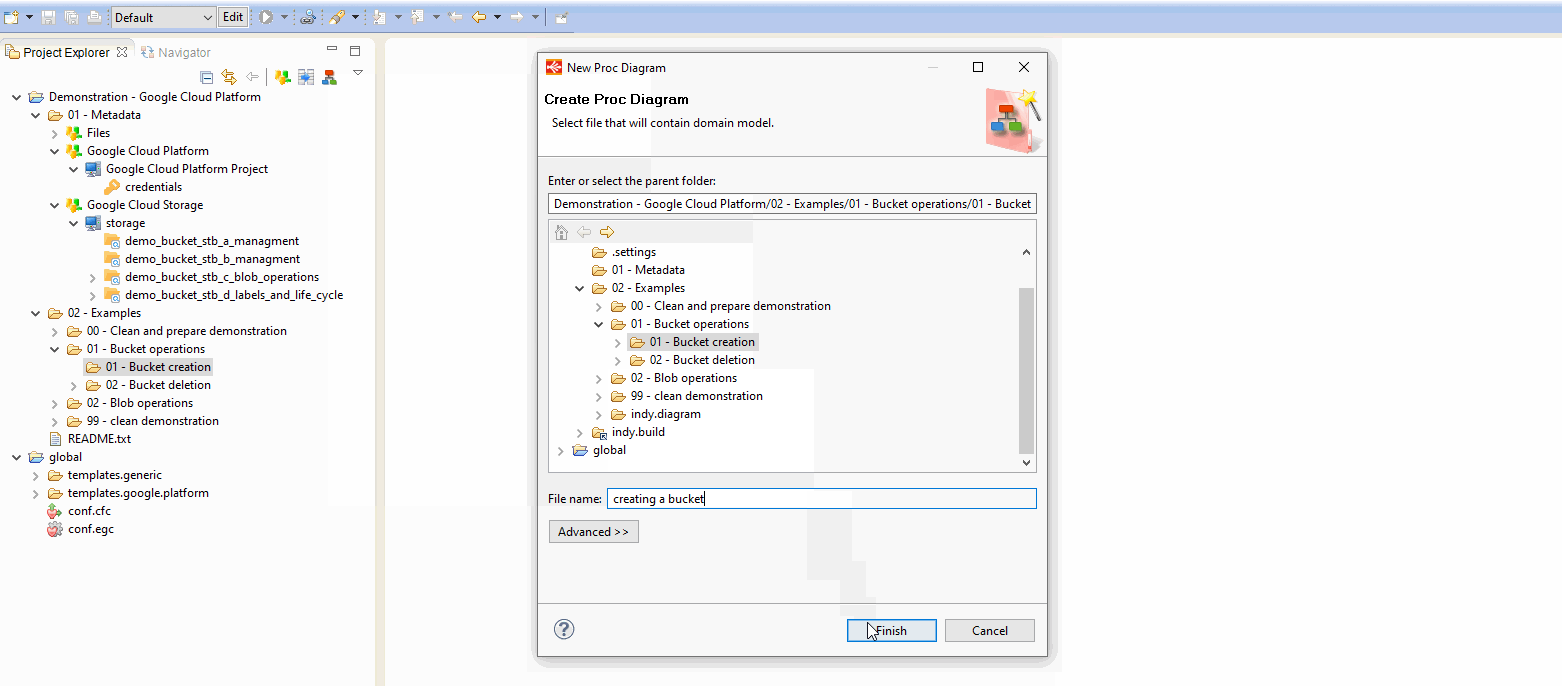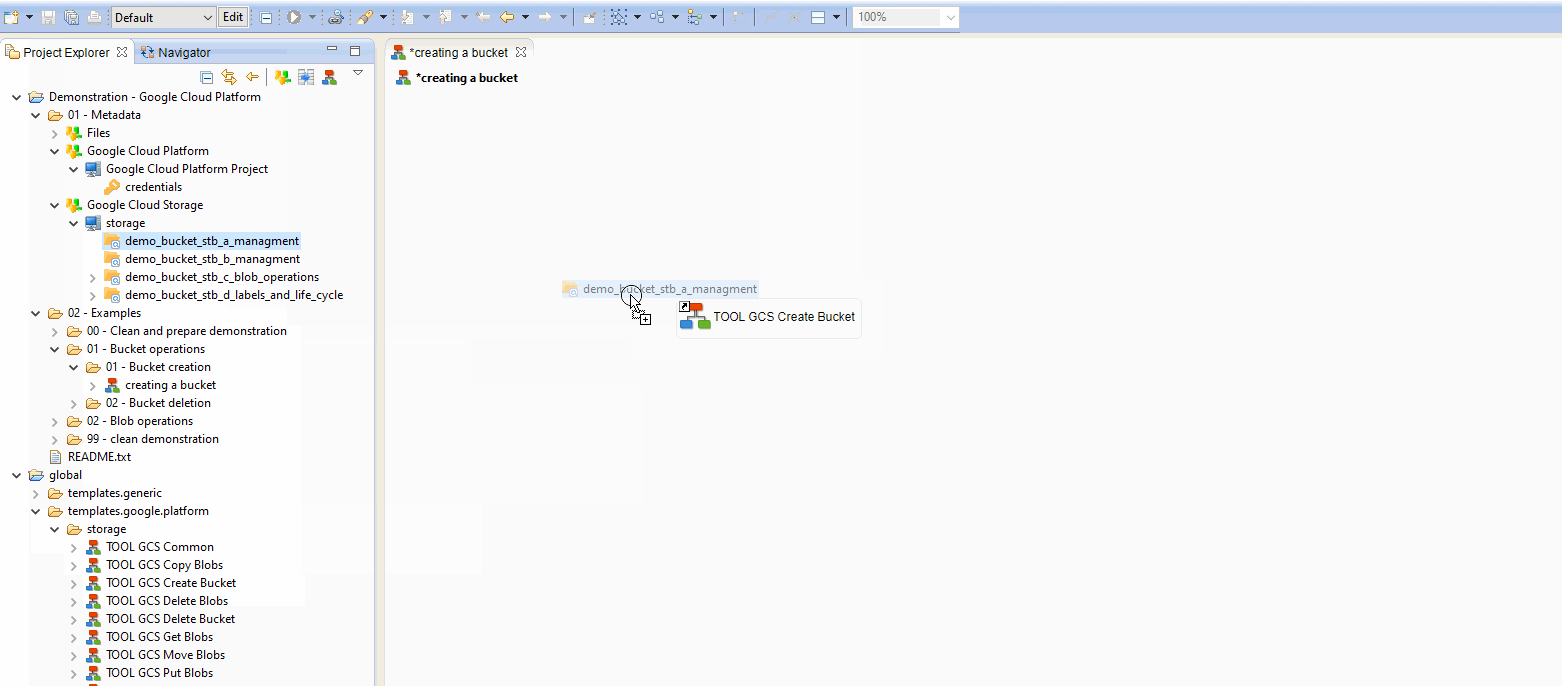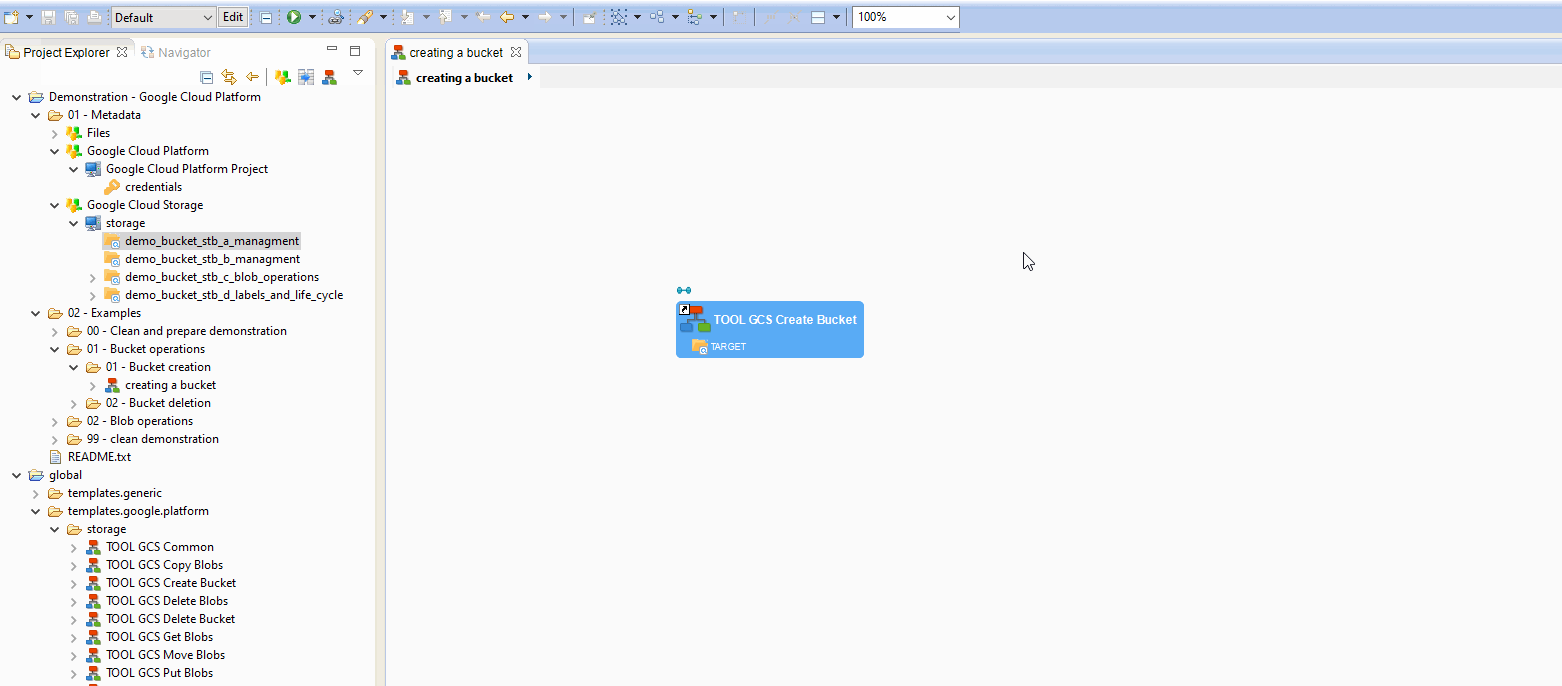
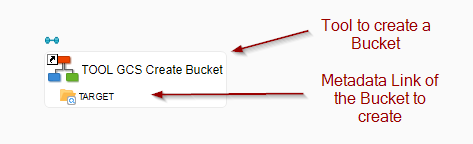
Example of Process for creating a Bucket
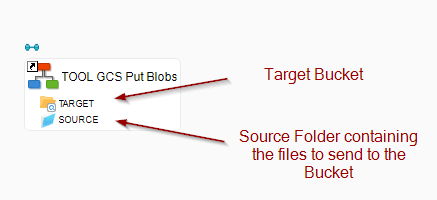
Example of Process for sending a bunch of files into a Bucket
Example of Process for retrieving a bunch of files from a Bucket
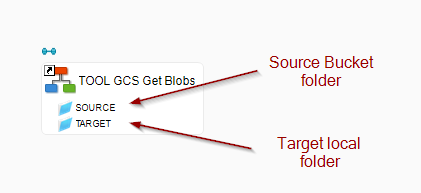
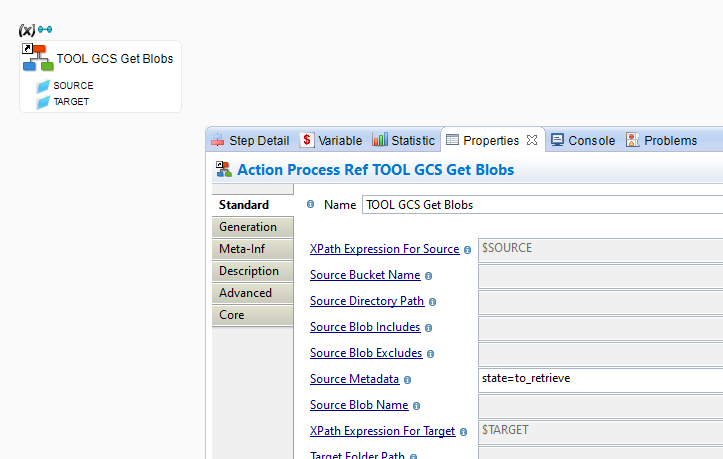
Example of Process for retrieving a filtered list of files from a Bucket, filtered using Blob Metadata Properties
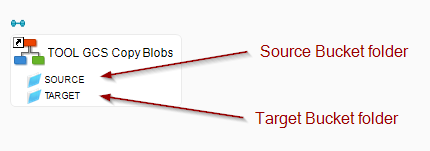
Example of Process for copying Blobs from one folder to another folder
Demonstration Project
A demonstration project presenting common and advanced usage of the Google Cloud Storage Connector in Stambia can be found on the download page.
You can download and import it in your workspace and then have a look at Processes examples.
It is a good start to familiarize with its usage and to see how the Metadata are configured, for instance.